There are multiple ways hackers and malicious actors can simultaneously use to gain unauthorized access to information. That includes phishing emails, malware, or decoding techniques. For instance, hackers may deceive users into clicking a fake link disguised as an official organization or to steal unencrypted login credentials from public Wi-Fi. Furthermore, they can exploit software vulnerabilities to implant ransomwares and extort money.
Hackers use the stolen information to commit crimes, depending on the amount of data they obtain from victims. Often, cybercriminals appropriate victims’ bank details to make payments or apply for credit cards, changing victims’ billing addresses to keep them unaware of the crime. A more severe case is identity theft, where accounts are taken over or misused to conceal further crimes.
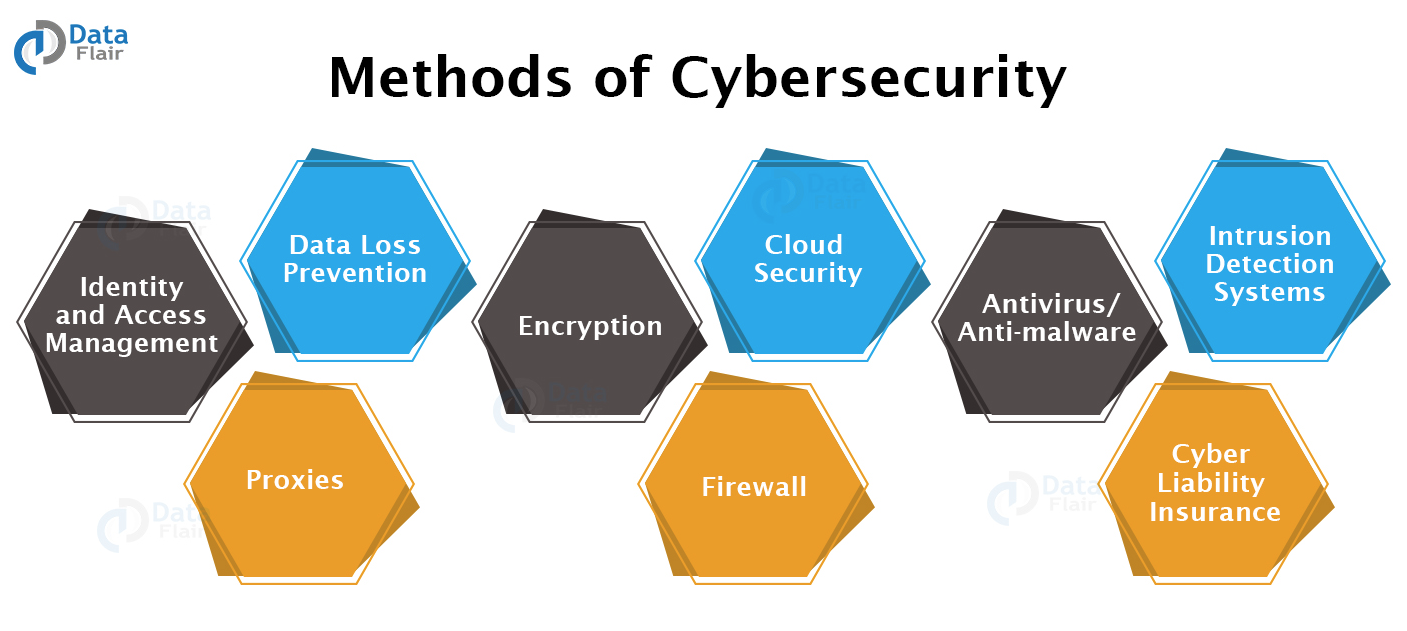
To prevent falling victim of cyberattacks, corporations and private entities often employ multiple security measures to strengthen their cyber resilience: implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly updating software patches, and encrypting sensitive documents. Training employees is also crucial to raise awareness of these threats, while designing an access control framework can minimize data exposure. Though the methods listed above do not guarantee complete protection against cyberattacks, developing a solid sense of cybersecurity is essential for ensuring smooth and safe business operation.